Optical Crosstalk in CMOS Image Sensors
Chris Fesenmaier and Benjamin Sheahan
Psych 221 - Winter 2006-2007
| Welcome | ||
| Introduction | ||
| Methods | ||
| Pixel Scaling | ||
| Methods | ||
| Results | ||
| Conclusions | ||
| References | ||
| Crosstalk Reduction | ||
| Methods | ||
| Air Gaps | ||
| Light Guide | ||
| Metal Mirrors | ||
| Results | ||
| Reference | ||
| Air Gaps | ||
| Light Guide | ||
| Metal Mirrors | ||
| Conclusions | ||
| References | ||
| Appendices | ||
Results - Reference
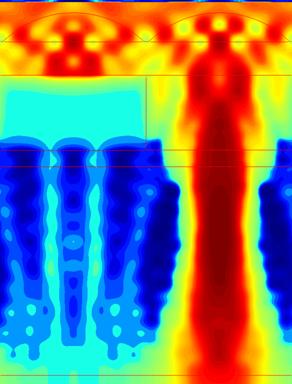
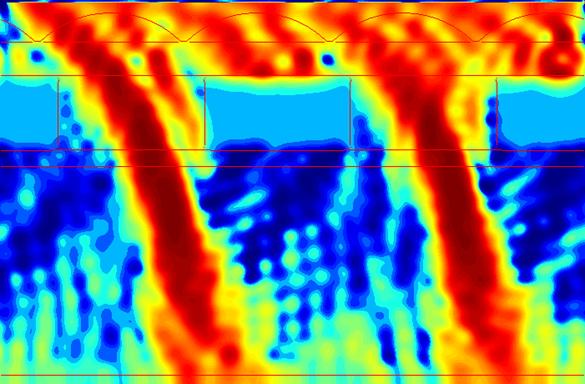
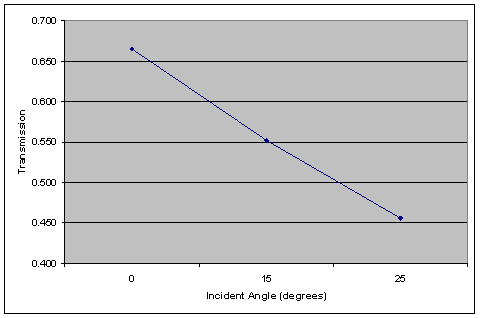
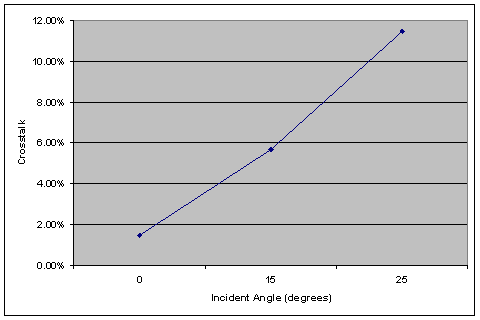
As the Poynting vector plots show, there is a significant amount of diffraction that causes the light to spread out, even at normal incidence. The spreading is amplified at off-axis incidence, as can be seen in Figure 8. All Poynting vector plots have been enhanced to bring out detail; although it may appear that light is leaking through the black filter, the actual power is negligible. Note that the transmission decreases and crosstalk increases significantly with increasing angle, even with a rough optimization of the microlens and color filter shift.
|
Fig. 7. Poynting vector plot for the reference pixel for normal incidence. |
|
Fig. 8. Poynting vector plot for the reference pixel at 25° incidence. |
|
(a) |
|
(b) |
Fig. 9. Transmission (a) and crosstalk (b) versus incident angle for the reference pixel. |