Primary-Consistent Soft-Decision Color Demosaicking
This algorithms is developed by X.Wu and N.Zhang [2].
Objective of Algorithm
In a lot of demosaicking algorithms, missing color components at a pixel are interpolated independently of the color interpolation at neighboring pixels. The interpolation decision is made on a hypothesis of the local gradient, but this hypothesis is not verified after color interpolation is completed. The PCSD algorithm aims to examine the interpolation results under the horizontal and vertical hypothesis in a local window, and choose the one whose underlying hypothesis agrees with the reconstructed color image best. It interpolates missing primary color components of a pixel in a consistent direction and determines the interpolation direction via soft decision.
The block diagram of the algorithm is shown below, and details of the algorithm are explained later.
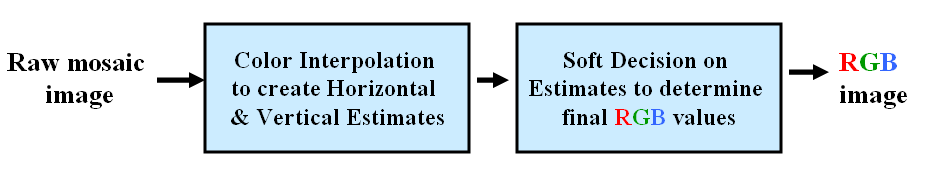
Detailed Explanation of the Algorithm
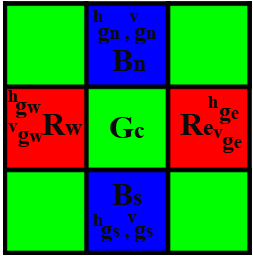
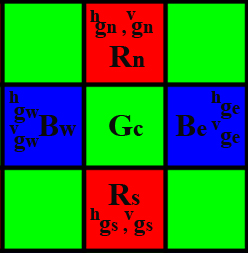
The Bayer Pattern below will serve as a reference for how positions are referenced in all the equations.
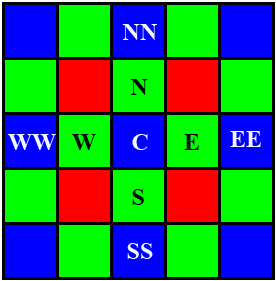
I. Color Interpolation
1.Interpolation of Missing G Values
First missing green values at red sampling points are interpolated using the equations below.
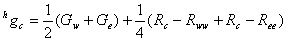
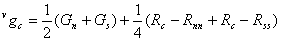
For interpolating missing green values at blue samples, equation is same as above except R is replaced with B.
2. Interpolation of Missing R/B Values at G Sampling Positions
Interpolation of missing red and blue values at green sampling positions ca be divided into 2 subcases.
Subcase 1 : G sampling positions with horizontal R and vertical B neighbors.
The figure below shows the situation represented by subcase 1
Missing red or blue values at these sampling points are found using the equations below
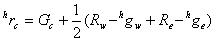
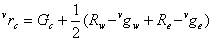
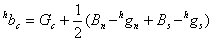
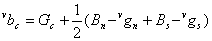
Subcase 2: G sampling positions with horizontal B and vertical R neighbors.
The figure below shows the situation represented by subcase 1
Missing red or blue values at these sampling points are found using the equations below
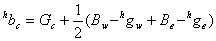
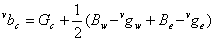
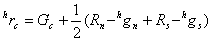
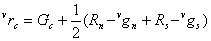
3.Interpolation of missing R/B Values at B/R Sampling Positions
Estimating the missing red/ blue values at the red/blue sampling points is one of the most challenging steps in a demosaicking algorithm. This is because the red/blue color is not sampled at all in both the current row and current column. Missing red or blue values at these sampling points are found using the equations below
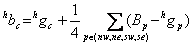
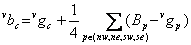
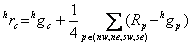
At this point the vertical and horizontal estimates of all missing color values have been found.
II. Soft Decision on Estimates
1. Find primary difference under horizontal and vertical hypothesis
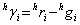 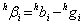
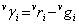 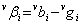
For each pixel i , a primary difference pair for horizontal estimate 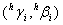 and vertical estimate and vertical estimate 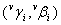 are formed. Then 4 horizontal and vertical gradient measures are measured for each pixel. Assume an array where each cell represents the primary difference pair of the pixel. are formed. Then 4 horizontal and vertical gradient measures are measured for each pixel. Assume an array where each cell represents the primary difference pair of the pixel.
2. 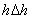 for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below
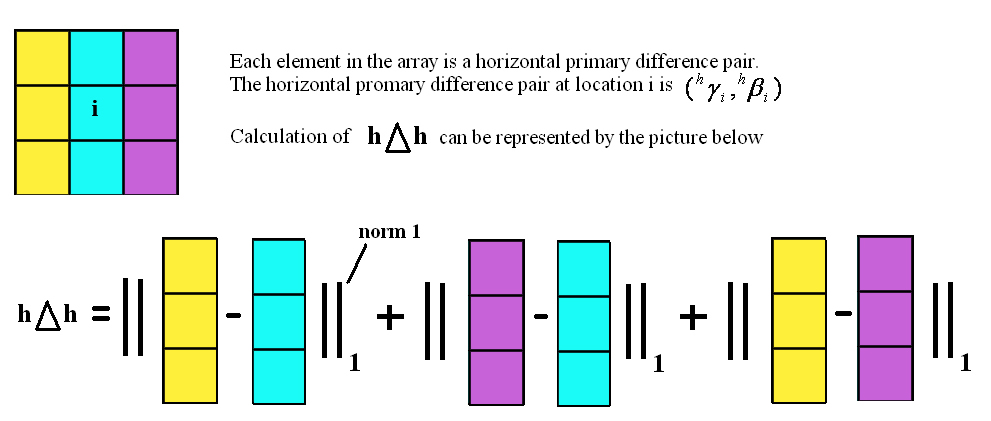
3. 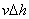 for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below
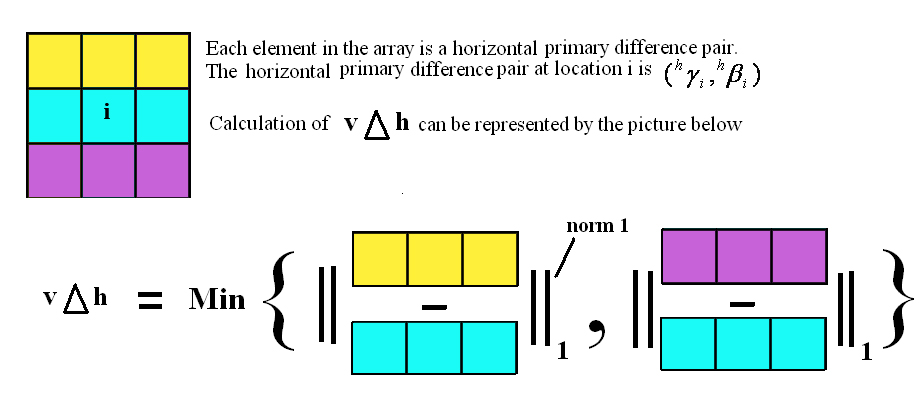
4. 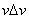 for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below
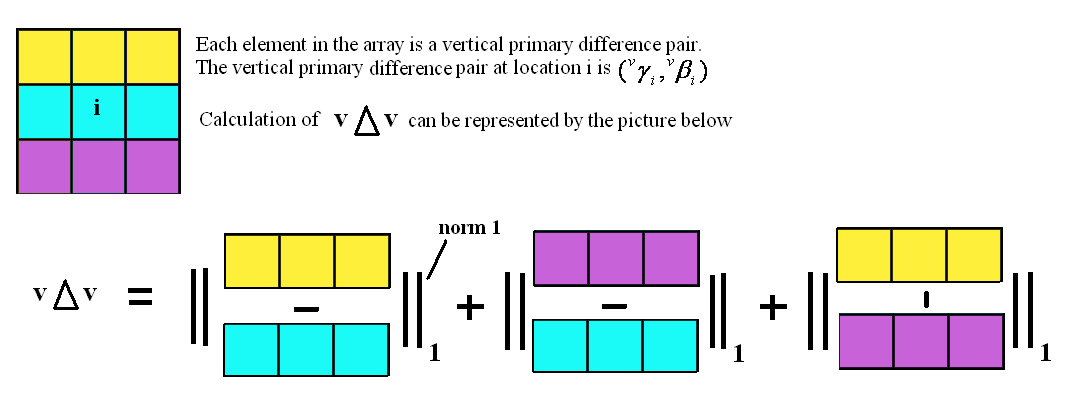
5. 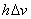 for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below for a pixel i is formed from the diagram shown below
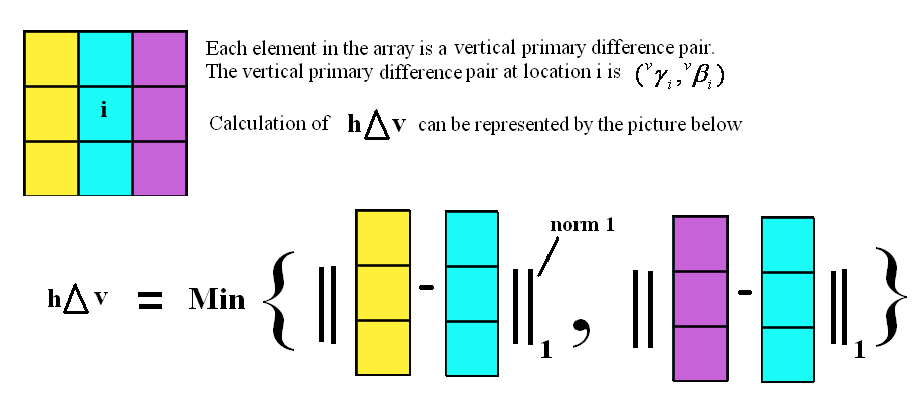
6. Soft Decision
Finally, setting z = [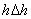 , ,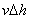 , ,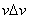 , ,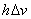 ] ]
Whether the horizontal or vertical estimate is used for each pixel is chosen by the criteria
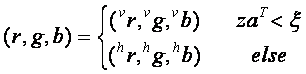
where a = [-0.62, -0.35, +0.62, +0.35] , 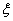 = 0 = 0
|