PSYCH221: A survey of digital watermarking techniques
|
Introduction: Methods: Conclusion: Contacts: |
Methods
Image Adaptive - Discrete Cosine
Transform (IA-DCT)
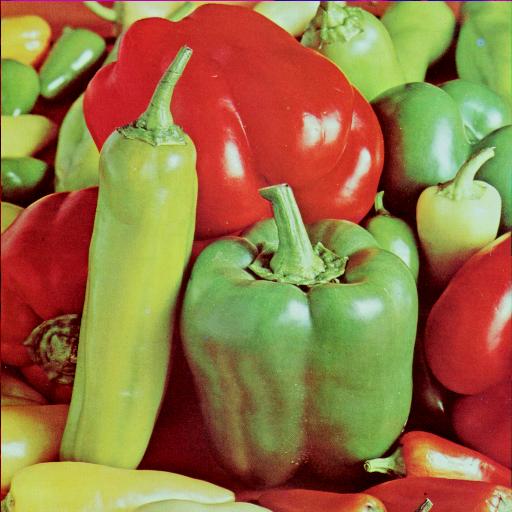
IA-DCT extends the spread spectrum method by introducing local adapatability. In spread spectrum, the frequencies in an image are examined on a global level. Additionally, spread spectrum uses a constant weighting factor when adding a watermark to each of the DCT coefficients. [9] describe an image-adaptive technique based on an 8x8 DCT. This approach allows for local control. The similarity to JPEG compression allows this method to be integrated easily into an existing JPEG image without decompression. In lieu of a fixed parameter, each 8x8 tile is weighted by a just-noticeable-difference (JND) function first described in [12]. This function uses an empirical model that accounts for the luminance and contrast masking properties of the human visual system. The results look excellent, with no noticeable distortion. The error appears to mirror the image. After encoding, the watermark can be detected in a similar fashion as the spread spectrum method. The plots below show the result of watermark detection after applying a 50% image resize as well as JPEG compression. The 50th element represents the real watermark. The other elements represent other, randomly generated watermarks. 
Encoded image after shrinking by 50% 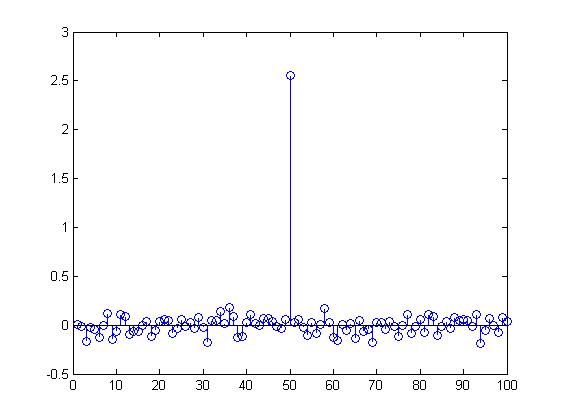
Watermark detection from resized image 
Encoded image after JPEG compression 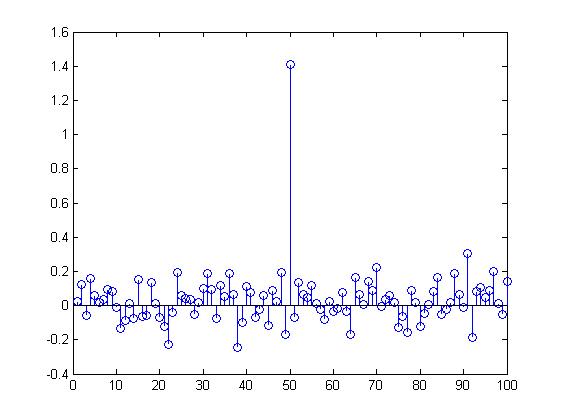
Watermark detection after JPEG compression with quality=10 |


