Home | Introduction | Background | Schemes | Conclusion | References | Appendix
Background
Single-User Foveated Video
A perceptually-faithful video foveation architecture has been developed by Geisler and Perry [2]. Their publications and software are available online at http://fi.cvis.psy.utexas.edu/.
We now describe one way of operating their system. For each frame of video, the encoder constructs several coarser and coarser representations by repeatedly applying an anti-aliasing filter and subsampling. Then, given information about the viewer's direction of gaze and distance from screen, it determines to which level of spatial resolution each part of the image needs to be rendered. Finally, the encoder upsamples, interpolates and blends the various representations of the original frame according to this spatial resolution map.
Since the foveation encoder described above outputs video in standard frame-by-frame format, it can be easily concatenated with a conventional video encoder, such as an H.264 encoder. The fact that the frame output of the foveation encoder diminishes in high frequency content away from the foveation center means that the concatenated structure results in compression gains over unfoveated video compressed at the same quality.
Simulation
We applied the foveation encoder with a moving foveation center to a raw video sequence. Figures 2 and 3 show the first frames of the unfoveated and foveated sequences, respectively. Click on an image to access its respective video sequence in .AVI format.
Figure 2: Frame 1 of unfoveated Bus sequence. Click on image to access sequence in .AVI format.
Figure 3: Frame 1 of foveated Bus sequence. Click on image to access sequence in .AVI format.
Next, we compressed these two sequences at different compression qualities. The resulting bandwidths are shown in Figure 4 on a log scale. We demonstrate that for this video sequence, foveation can consistently produce a factor of 3 compression improvement over a range of bandwidths.
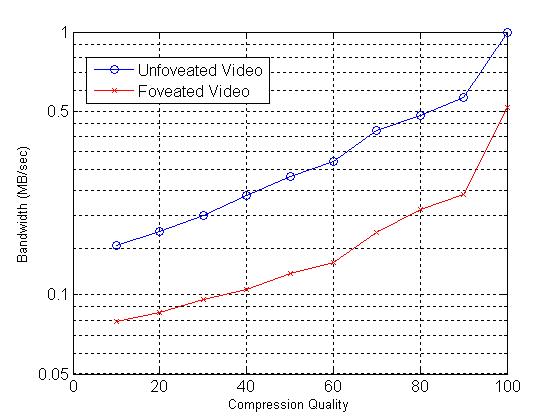
Figure 4: Comparison of compression performance for unfoveated and foveated video sequences