Types of Stereograms

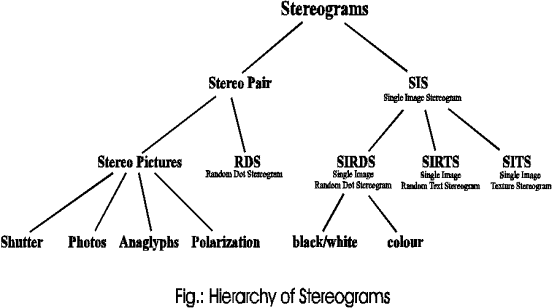
Stereogram:
A stereogram is any stereoscopic image.
Stereo Pair:
Stereograms consisting of two images.
Stereo Pictures:
A pair of images taken from two different viewing points. Wheatstone invented the technique of stereo pairs. With the invention of photography, stereo photography was developed.
RDS:
Random dot stereogram is a stereogram with a random pattern instead of a texture. In 1972, Julesz published random dot stereograms for the first time. When you see such a picture, it looks like a random dot pattern without any additional information. The development of this kind of stereograms became possible by advanced computer techniques.
Shutter:
Tachistoscopic techniques are defined by generating images for the left and right eye separated by shutter glasses. In order to create the three-dimensional illusion, the shutter obscures one eye's view while the other eye receives its respective image, thus flickering fast enough will create an image that should “pop” out. These techniques are highly employed in virtual reality systems.
Anaglyphs, Polarization Filters:
These methods are based on different colored or polarized images. A pair of spectacles gives each eye the proper information by special filter glasses. Many shows and movies are created through this type of stereogram.
Lenticular:
A lenticular is a thin, portable, full color stereo picture. It is created with thin plastic lenses placed over the photograph restricting the view of each eye to a particular part of the picture. Lenticulars can be composed on a computer, but can not viewed on a computer without the aid of expensive specialized attachments.
Autostereograms (No hardware is needed to view)
SIS:
Single image stereograms. In 1979, Christopher W. Tyler presented the world's very first single image stereogram. Currently, the single image stereograms is what rekindled the craze of three-dimensional images.
SIRDS:
Single image random dot stereogram is a single image random dot stereogram
with a random pattern instead of a texture.
They are derived from Julesz’ original idea. They consist of a random pattern of dots, each representing
two pixels of the object.
SIRTS:
Single image random text stereogram is a single image stereogram with ASCII text, thus limiting resolution of the image.
SITS:
Single image texture stereogram is a single image stereogram using a texture instead of a random pattern.
