Background Information –
Lens Aberrations
There are several ways by which lenses can distort an
image. Firstly, a lens can cause blurring, a condition under which the light is
not completely focused. This is an effect that is wavelength-dependent and is
well known as chromatic aberration. This is also an effect that can depend on
the position of the light in the field of view.
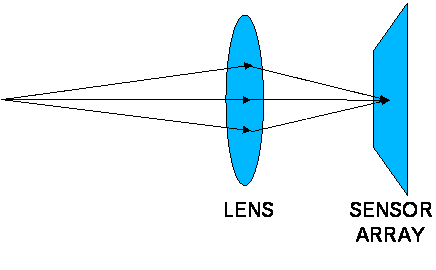
Figure 1: Simple model used for a digital imager.
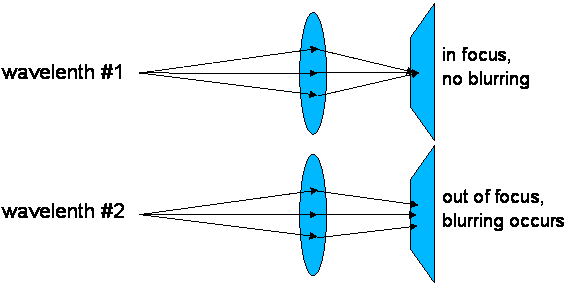
Figure 2: Wavelength-dependent
aberration in lenses (chromatic aberration)
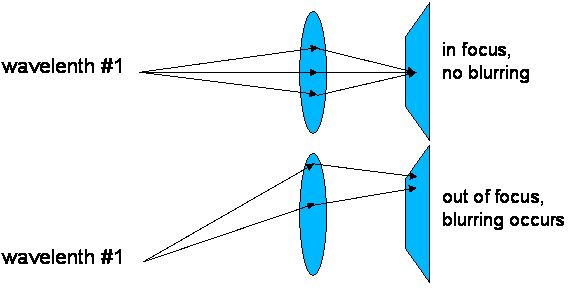
Figure 3: Position-dependent aberration
in lenses
A aberration that is
caused by lenses is photon reflection. Depending on the index of refraction of
the lens, not all of the incident light will be transmitted through the lens.
This is also an effect that is a function of the wavelength of the light (this
is because the index of refraction is wavelength-dependent). Since the angle of
incidence of incidence also matters, this aberration is also position-dependent
(the position of the light in the field of view).
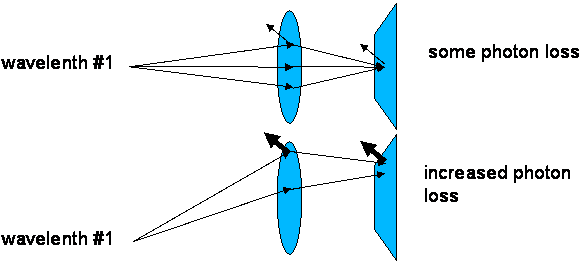
Figure 4: position-dependent photon
scattering of image sensors. Image sensors also exhibit wavelength-dependent
photon scattering (not shown in figure).
In
summary, the lens aberrations discussed are categorized in the following table.
|
|
Blurring |
Photon Loss |
|
Wavelength-Dependent |
x |
x |
|
Position-Dependent |
x |
x |