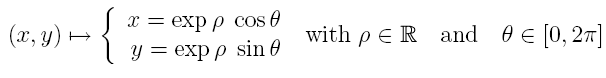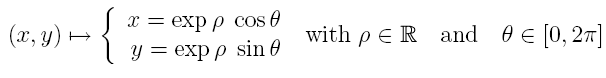Domain for performing Watermarking
The watermark algorithm can be carried out in the spatial domain, the normal case. However as seen
before (in the Transform Domain techniques in Steganography) using the frequency domain has
certain advantages.
Discrete Cosine Transform
The most common workspace is the frequency doman using the DCT. We have
covered this earlier in Steganoraphy and also in the spread-spectrum technique in watermarking
and explored that altering perceptually significant DCT coefficients is a good watermarking
approach.
Discrete Fourier Transform
The DFT, similar to DCT, brings us into the frequency domain. Furthermore, the DFT can also
be used for phase modulation between the watermark and its cover (covered in the section
on merging watermark and cover bits) and can also be used to split the image
into perceptual bands to store the watermark in.
Mellin-Fourier Transform
Most watermarking algorithms have problems in extracting the watermark after an affine geometric transformation
has been applied to the watermarked image. To overcome this, O.Ruanaidh et al[17] have proposed
the use of the Mellin-Fourier Transform for watermarking.
The MFT is based on the translation property of the Fourier Transform. That is to say,
f(x1+a, x2+b) = F(k1+k2) exp(-i(ak1 + bk2))
This makes sure that only phase is altered by a translation. For rotation and zooming O.Ruanaidh proposed
the use of a log-polar mapping in which the rotation of any element (x,y) in cartesian coordinate
will result in translation in the log-polar mapping space.
Using a modification of the coordinate system, both rotation and zoom can be reduced to a translation. The property
of translational invariance can be then used to construct a space insensitive to any rotation zoom operations carried
out on the watermarked object
Wavelet Domain
A current popular method appears to be to use the wavelete domain to perform watermarking. I did not go into
the implementatio of the same due to time and resource constraints but the basic idea behind using wavelets
is their advantages which are similar to the DCT with the added one of possessing multiresolutional aspects
in the wavelet domain. There is a growing body of literature on using wavelets for watermarking[20][21][22]