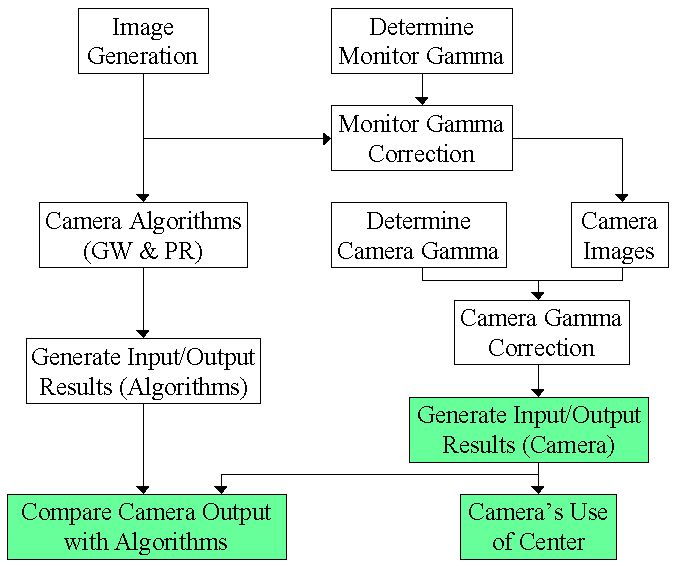
- Determine Monitor Gamma
- In order to perform a realistic comparison between the input images and final images, the
scale must stay linear. This means that the linear input images must be displayed on the
monitor on a linear scale. Images displayed on a monitor are altered by the monitor's
gamma table. To correct for this, the images must pass through the inverse monitor gamma
function before being sent to the monitor. This requires obtaining the monitor gamma
function.
- In order to perform a realistic comparison between the input images and final images, the
scale must stay linear. This means that the linear input images must be displayed on the
monitor on a linear scale. Images displayed on a monitor are altered by the monitor's
gamma table. To correct for this, the images must pass through the inverse monitor gamma
function before being sent to the monitor. This requires obtaining the monitor gamma
function.
- Image Generation
- Several images are required to analyze the digital camera's color balancing functionality.
The idea behind these images is to create a know target color and vary the background color
to vary the ambient light. These images are grouped into two sets, images with and images
without a center target.
- Several images are required to analyze the digital camera's color balancing functionality.
The idea behind these images is to create a know target color and vary the background color
to vary the ambient light. These images are grouped into two sets, images with and images
without a center target.
- Monitor Gamma Correction
- Once the images have been created, this step prepares them for display on the monitor. The
original images in a linear scale are converted to a non-linear scale using the inverse
monitor gamma function. This causes the images to be displayed on the monitor with a linear
scale.
- Once the images have been created, this step prepares them for display on the monitor. The
original images in a linear scale are converted to a non-linear scale using the inverse
monitor gamma function. This causes the images to be displayed on the monitor with a linear
scale.
- Camera Algorithms
- Once the input images are generated and done the inverse gamma
monitor gamma correction, they are cycled through and run for
color balancing algorithms. This process includes reading in
image data, converting it to R, G & B values, running color
balancing algorithm functions, and writing the results to
output images. The 2 color balancing algorithm evaluated in
this project are Gray World and Perfect Reflector.
- Once the input images are generated and done the inverse gamma
monitor gamma correction, they are cycled through and run for
color balancing algorithms. This process includes reading in
image data, converting it to R, G & B values, running color
balancing algorithm functions, and writing the results to
output images. The 2 color balancing algorithm evaluated in
this project are Gray World and Perfect Reflector.
- Determine Camera Gamma
- In order to compare the output of color balancing algorithms
with camera output, we need to cancel out the camera function
except color balancing. In this project, we assume all other
camera functions other than color balancing can be approximate
as gamma function. To cancel out other functions of camera,
the output images of camera must pass through the inverse
camera gamma correction before being compared with algorithm
output. Also the camera gamma correction has been done for R,
G & B separately. Thus the camera gamma functions has to be
obtained for R, G & B respectively.
- In order to compare the output of color balancing algorithms
with camera output, we need to cancel out the camera function
except color balancing. In this project, we assume all other
camera functions other than color balancing can be approximate
as gamma function. To cancel out other functions of camera,
the output images of camera must pass through the inverse
camera gamma correction before being compared with algorithm
output. Also the camera gamma correction has been done for R,
G & B separately. Thus the camera gamma functions has to be
obtained for R, G & B respectively.
- Camera Images
- Once the images have been preparted for display on the monitor, they are cycled through and
shoot with the camera. This process involves setting up the camera to take images on a
monitor which has a refresh rate that would normally result in bars in the image. During
this step, 264 images from the two image sets are shoot.
- Once the images have been preparted for display on the monitor, they are cycled through and
shoot with the camera. This process involves setting up the camera to take images on a
monitor which has a refresh rate that would normally result in bars in the image. During
this step, 264 images from the two image sets are shoot.
- Camera Gamma Correction
- In addition to the monitor gamma conversion, the digital camera also performs a gamma
conversion. Analysis of the camera images requires them to be in a linear scale.
This requires the camera gamma conversion to be corrected for after the images have
been shoot before they can be analized.
- In addition to the monitor gamma conversion, the digital camera also performs a gamma
conversion. Analysis of the camera images requires them to be in a linear scale.
This requires the camera gamma conversion to be corrected for after the images have
been shoot before they can be analized.
- Generate Input/Output Results (Algorithms) -- Gray World & Perfect Reflector
- Once the output images of Gray World and Perfect Reflector color
balancing algorithms have been generated, they are compared to
the input images. This comparison involves calculating the
difference between the input image target colors and the final
image target colors. These differences are then plotted
relative to the original image background colors. This results
in four plots, R, G, B & Gray, which describe the color balancing
results of Gray World and Perfect Reflector algorithms.
- Once the output images of Gray World and Perfect Reflector color
balancing algorithms have been generated, they are compared to
the input images. This comparison involves calculating the
difference between the input image target colors and the final
image target colors. These differences are then plotted
relative to the original image background colors. This results
in four plots, R, G, B & Gray, which describe the color balancing
results of Gray World and Perfect Reflector algorithms.
- Generate Input/Output Results (Camera)
- Once the images shoot by the camera are corrected for the camera's gamma conversion,
they are compared to the original images. This comparison involves calculating the
difference between the original image target colors and the final image target colors.
These differences are then plotted relative to the original image background colors.
This results in three plots, R, G and B, which describe the camera's color balancing
results.
- Once the images shoot by the camera are corrected for the camera's gamma conversion,
they are compared to the original images. This comparison involves calculating the
difference between the original image target colors and the final image target colors.
These differences are then plotted relative to the original image background colors.
This results in three plots, R, G and B, which describe the camera's color balancing
results.
- Compare Camera Output with Algorithms
- Once the difference results of algorithms and camera are available,
they are compared by taking difference of them, then plotted.
This results four plots, R, G, B & Gray, which describe the
camera output is close to which algorithm.
- Once the difference results of algorithms and camera are available,
they are compared by taking difference of them, then plotted.
This results four plots, R, G, B & Gray, which describe the
camera output is close to which algorithm.
- Camera Use of Center
- Cameras are designed to maximize power usage and decrease delay. A technique which would
help optimize these camera properties would be to decrease the amount of processing used
during color balancing. This can be accomplished by only analyzing the center of the image
to perform color balancing.
- Cameras are designed to maximize power usage and decrease delay. A technique which would
help optimize these camera properties would be to decrease the amount of processing used
during color balancing. This can be accomplished by only analyzing the center of the image
to perform color balancing.
trek@alumni.stanford.edu lihui@leland.stanford.edu