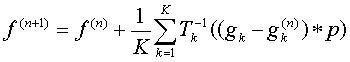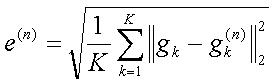Irani and Peleg Iterative Method
This method is concerned with solving the following equation:
.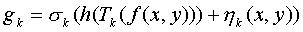
where
-
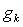 = sensed image
of he kth frame
= sensed image
of he kth frame
-
f = high resolution image in a desired reconstruction
view. Finding f is the objective of the super-resolution algortihm
-
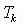 = the 2D transformation
from f to
= the 2D transformation
from f to 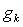 as determined by affine transformation (assumed to be invertible)
as determined by affine transformation (assumed to be invertible)
-
h = a blurring operator determined by the (Gaussian) PSF
-
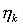 = an additive
noise term
= an additive
noise term
-
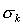 = downsampling
operator to go from SR dimensions to LR dimensions
= downsampling
operator to go from SR dimensions to LR dimensions
The main feature of the Irani and Peleg method is that it iteratively uses
the current best guess for the SR image to create LR images and then compare
the simulated LR images to the original LR images. These difference
images (found by subtracting real LR - simulated LR) are then used to improve
the initial guess by "backprojecting" each value in the difference image
onto the SR image. This results in an improved SR image.
We now introduce
-
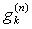 as the nth
iteration of the simulated version of the kth frame
as the nth
iteration of the simulated version of the kth frame
-
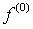 as the inital
guess for the SR image
as the inital
guess for the SR image
-
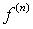 as the nth iterative
guess for the SR image
as the nth iterative
guess for the SR image
-
K as the number of LR images
-
p as a backprojection kernel determined by the equation
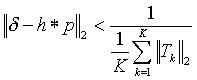 where
where 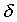 is
the unity pulse centered at (0,0)
is
the unity pulse centered at (0,0)
The iterative method is to then use the following equations for the most
ideal resolution on f
.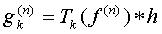
.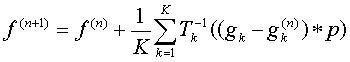
We can additionally define an error function which we wish to minimize
.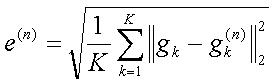
![]()
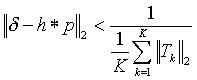 where
where