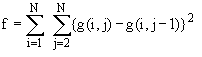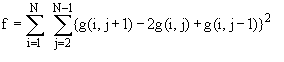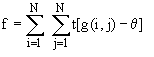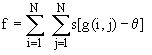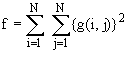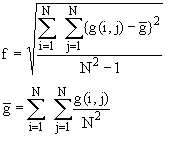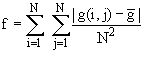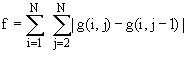
b) Threshold Absolute Gradient
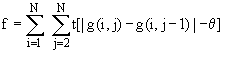
By summing those differences larger than a certain threshold value, only
those larger gradients representative of the focused situation are taken
into account.
c) Squared Gradient
By squaring, the algorithm enhances the larger gradients over the smaller
ones. The advantage of this function over method c) is that it has no
threshold to adjust.
d) Laplacian
In the fourier domain, the transfer function of a 2nd order diference
filter (laplacian) suppresses more strongly the lower spatial frequencies
than the first order difference filter (gradient).
e) Threshold Video Signal Content
Originally devised for microscopes. According to
researchers, the threshold setting affects only the shape of the extremum,
not its position.
f) Threshold Video Signal Pixel Count
Count the number of grey values above the threshold setting.
g) Signal Power
h) Standard Deviation
i) Normalised Standard Deviation
Divide the equation for h) by the mean of g(i,j).
Division by the mean compensates for changes in the average image
brightness.
j) Absolute Variation
Simplier than the standard variation method
k) Normalised Absolute Variation
Divide the equation for j) by the mean of g(i,j).